In recent years, thermal scopes have become increasingly popular among hunters, shooters, and outdoor enthusiasts. This is because the scope provides a significant advantage in low-light or nighttime conditions, allowing users to see clearly and accurately where traditional scopes may fall short. A thermal scope works by detecting the body heat of a target and displays an image of that heat on the scope’s screen. This makes it easy for users to identify their target, even in complete darkness, as long as there is some heat being emitted from the target.

The benefits of using a thermal scope on a rifle are numerous and can greatly enhance a user’s experience in night hunting or shooting. These benefits go beyond improved accuracy and success rates which are found in every other kind of scope. It extends to areas such as safety, versatility, and efficiency. In this article, we will explore some of the key benefits of using a thermal scope on a rifle and provide real-life examples of how they have been used to improve hunting and shooting experiences. Before then, let’s start with how it works and the types.
How Thermal Technology Works
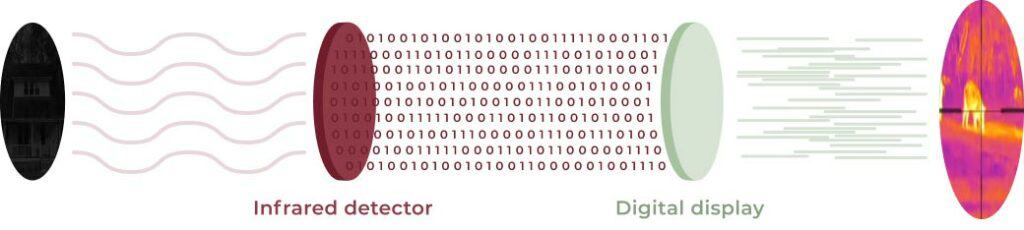
A thermal scope works by detecting the heat signatures of objects and people. It does this by detecting and measuring the infrared radiation emitted by objects. The thermal scope’s lens collects this infrared radiation, which is focused onto an infrared detector made up of tiny sensors called microbolometers.
Each microbolometer measures the temperature of a small area of the scene and converts this information into an electrical signal. The signals from each microbolometer are then combined and processed by the thermal scope’s computer, which generates an image that is displayed on the thermal scope’s screen. Different colors or shades of gray indicate different temperatures, with warmer objects appearing brighter or white and cooler objects appearing darker or black.
Types of thermal scope
There are two main types of thermal scopes: standalone and clip-on.
Standalone Thermal Scopes
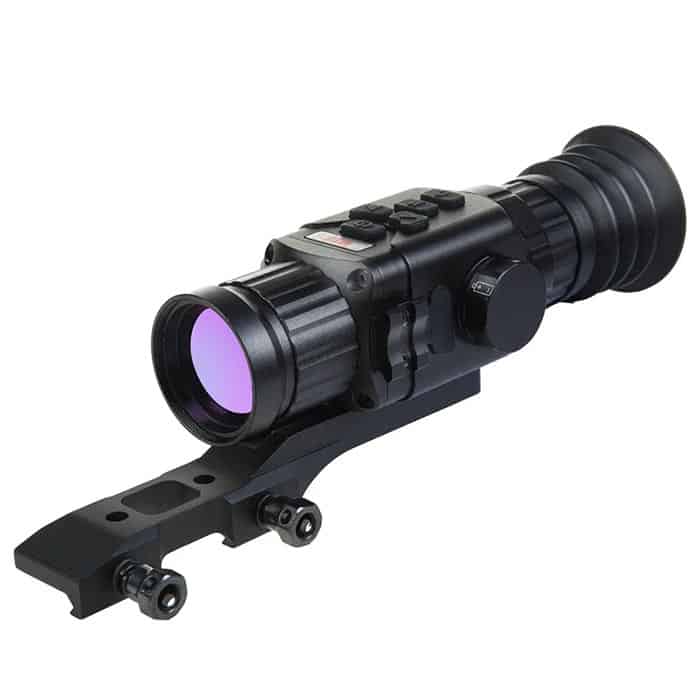
Standalone thermal scopes are designed to replace traditional rifle scopes and are mounted directly onto the rifle. They provide the shooter with a clear thermal image of their target, allowing for accurate shots even in low-light conditions. Standalone thermal scopes are available in a wide range of magnifications and price points, making them a popular choice among hunters and shooters.

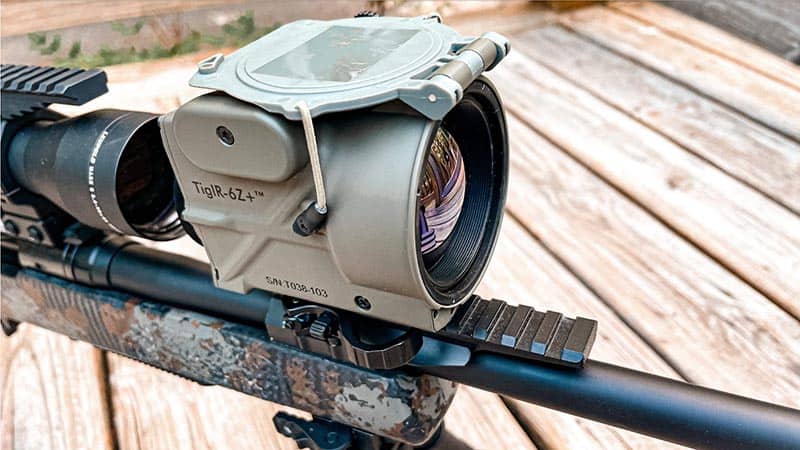
Clip-On Thermal Scopes
Clip-on thermal scopes are designed to be attached to an existing daytime rifle scope. They use a separate thermal imaging device that clips onto the front of the daytime scope, allowing the shooter to switch between thermal and daylight imaging as needed. Clip-on thermal scopes are a more cost-effective option compared to standalone thermal scopes, and they provide the user with more versatility in the field.

In addition to these two main types of thermal scopes, there are also hybrid scopes that combine traditional optical lenses with thermal imaging capabilities. These scopes are designed to provide the user with the best of both worlds and are ideal for those who want to maintain a clear image during the day and have thermal imaging capabilities at night.
When choosing a thermal scope, it’s important to consider factors such as resolution, range, battery life, and overall durability. It’s also important to consider the type of hunting or shooting you will be doing, as different types of thermal scopes may be better suited for different scenarios. Ultimately, the right thermal rifle scope will depend on your individual preferences.
How a thermal scope can benefit shooters
Improved accuracy
A thermal rifle scope provides improved accuracy in low light conditions, making it easier to hit your target. This can be especially useful for hunters who need to track the game at night. For example, a hunter who is tracking a deer through the woods at dusk may struggle to see the animal clearly with a traditional scope. However, with a thermal scope, the hunter can detect the deer’s body heat and aim precisely, even under minimal light. This can result in a cleaner and more humane shot, reducing the chance of losing the game.
Enhanced situational awareness
With a thermal scope, you can detect targets in complete darkness or through obstacles such as foliage or smoke. This can be especially useful in tactical situations or in law enforcement operations. For example, a police officer who is responding to a call at night may struggle to see suspects who are hiding in the shadows or behind some objects. However, with a thermal scope, the officer can detect the suspect’s body heat and location, even in complete darkness. This can give the officer a tactical advantage and improve their safety.
Better target identification
A thermal imaging scope allows you to distinguish between living and non-living objects and reveals the presence of concealed weapons or other items. This can be useful in border security, law enforcement, and military operations. For example, border patrol agents may use thermal imaging technology to detect people attempting to cross the border illegally. A thermal imaging scope can help the agent differentiate between people and animals, reducing the chance of false alarms. Additionally, a thermal rifle scope can reveal the presence of weapons that may be hidden on a person’s body. This can improve the agent’s safety and the overall effectiveness of the border patrol operation.
Increased safety
By being able to detect threats at a distance, a thermal riflescope can help keep you safe in potentially dangerous situations. This scope can be useful for law enforcement, the military, and hunters who are operating in hazardous environments. For example, a military sniper who is observing a target from a concealed position may be able to detect enemy troops approaching from a distance using a thermal scope. This can give the sniper time to react and take appropriate action, improving their safety and the success of their mission.
Improved hunting success
With a thermal scope, you can track the game at night, giving you an advantage over your prey. This can be especially useful for hunting predators such as coyotes or feral hogs that are active at night. For example, a hunter who is using a thermal riflescope to hunt feral hogs may be able to detect the heat signature of a group of hogs in the darkness. The hunter can then approach the hogs without being detected and take a shot, increasing their chances of success. Additionally, a thermal optic can help hunters identify the best time and location to hunt based on the activity patterns of the animals they are targeting.
In both of these examples, a thermal imager provides a significant advantage over traditional sighting methods, allowing the user to detect and engage targets that may be difficult or impossible to see with the naked eye. This night vision technology can improve safety and effectiveness and increase the success of night hunting and wildlife management efforts.
Search and Rescue
In search and rescue operations, a thermal optic can help locate missing persons by detecting their body heat. This gadget can be most useful in wilderness search and rescue operations or in disaster response scenarios where people may be trapped under rubble or in other hazardous conditions at night. For example, a search and rescue team may use a thermal imager to locate a lost hiker who is stranded in the wilderness at night. The team can scan the area for body heat and quickly locate the missing person.
Surveillance
A thermal scope can be used for surveillance and monitoring in a variety of settings, including border security, wildlife management, and industrial operations. For example, a security team may use thermal technology to detect and monitor intruders attempting to breach a border or facility perimeter. The thermal device can detect body heat, even through obstacles such as smoke, and dust, and provide real-time surveillance footage to the security team. This can help prevent unauthorized access and improve overall security.
Wildlife observation
A thermal scope can be used to observe and study wildlife behavior in their natural habitat without disturbing or disrupting their activities. This can be useful for wildlife researchers, conservationists, and nature enthusiasts who want to study animal behavior and movements. For example, a wildlife researcher studying the behavior of nocturnal animals may use a thermal device to observe the animal’s movement patterns and behavior in the dark. This can provide valuable insights into animal behavior and improve conservation efforts.
Pest control
A thermal scope can be used for pest control and management, particularly for nocturnal pests such as mice and other rodents. By detecting the heat signature of these pests, a thermal imaging device can help pest control professionals identify the location of infestations and develop targeted control strategies. For example, a pest control professional may use a thermal scope to identify a rodent nest or burrow in a dark attic or basement. This can help them develop a targeted control strategy and reduce the overall population of pests in the area.
What Other Things Should You Consider
Factors
Here are some additional features to consider when learning about thermal scopes:
Battery life
Thermal scopes rely on batteries to function, so it’s important to choose a model with a long battery life or carry spare batteries with you.
Range
The effective range of a thermal scope can vary based on factors such as the quality of the device, weather conditions, and terrain. Choosing a scope with a range appropriate for the type of hunting or shooting you will be doing is important.
Price
Selecting a suitable thermal scope model that matches your requirements and budget is crucial, as the prices of these scopes can vary from hundreds to thousands of dollars.
Maintenance
Like any piece of equipment, thermal scopes require regular maintenance to function properly. This may include cleaning the lenses, storing the device properly, and always charging the batteries. Lack of maintenance can make the scope easily get faulty.
Things You Can See Through
Thermal scopes are designed to detect differences in temperature, which means they can see through certain types of environmental factors that may obscure visibility for traditional optics. Here are some examples of what thermal imaging technology can see through:
Smoke
Thermal scopes can see through smoke to detect the heat signature of objects or people that may be hidden from view.
Dust and blowing sand
If you are in the desert and it is very windy, you can still make good use of your thermal scope. Dust and blowing sand can significantly reduce visibility for other types of scopes, but thermal scopes can detect the heat signatures of objects or people through them.
Rain and snow
Rain and snow can also impact visibility, but thermal scopes can detect the heat signatures of objects or people, even in heavy precipitation.
It’s important to note that while thermal scopes can see through certain environmental factors, their effectiveness can be impacted by factors such as distance, the size of the object or person, and the temperature of the surrounding environment. Additionally, while thermal scopes can see through certain environmental factors, they may not provide a clear image in these conditions, as the thermal image may be distorted or blurry.
Things You Cannot See Through
While thermal scopes can detect the heat signatures of objects and people through certain environmental factors, there are also certain materials and conditions that they cannot see through. Here are some examples:
Walls, concrete, and glass
Thermal scopes cannot see through solid materials such as walls, concrete, or glass, as these materials block thermal radiation. Although you might have seen some scopes in the movie that could see through walls and concrete, I can tell you they are not thermal scopes.
Metal
Metals reflect thermal radiation, which means that thermal scopes cannot see through them.
Rocks and trees
Rocks and trees do not emit enough heat to register on a thermal scope, so they appear as dark or cool areas in the thermal image.
Underground
Thermal scopes cannot detect the heat signatures of objects or people that are located underground, as the soil and rock above them absorb the thermal radiation.
Water
Thermal scopes cannot see through water, as water absorbs and dissipates thermal radiation.
Human body
While thermal scopes can detect the heat signatures of humans, they cannot see through the human body to detect other structures.
It’s important to note that while thermal scopes have many benefits and can be a valuable tool in certain situations, they are not a substitute for caution, good judgment, and proper training. It’s always important to exercise care and safety when using any type of firearm or equipment.
Advantages of thermal technology over a night vision technology
Thermal scopes and night vision scopes are both used for low-light or nighttime conditions, but they operate on different principles and offer different advantages. Here are some advantages of thermal scopes over a night vision device:
Thermal scopes detect heat signatures
While a night vision device amplifies available light to produce a visible image, thermal scopes detect the heat signatures of objects and people. This means that thermal scopes can detect living beings and other objects that are not visible to the naked eye or to a night vision scope as long as some heat is emitted.
Thermal imagers work in total darkness
Unlike night vision devices, which require some ambient light to work, thermal scopes can detect heat signatures in complete darkness, which makes them ideal for operations that require stealth or secrecy.
Thermal imagers are less affected by environment
Night vision devices can be impacted by shadows and low-contrast areas, which can make it difficult to identify targets. Thermal scopes are less affected by shadows and low-contrast areas, as they detect heat signatures rather than light. Thermal scopes can also detect heat signatures through a fog, smoke, rain, and other environmental factors that can obscure visibility for a night vision scope.
Overall, thermal scopes offer several advantages compared to night vision scopes, particularly in complete darkness and in situations where environmental factors may impact visibility. However, night vision scopes are still a valuable tool in many situations, and the choice between the two depends on the specific needs and circumstances of the user.

Mike Hardesty is a published freelance gun writer. He also possesses specialized expertise in rifle scopes With dozens of articles and reviews published in Pew Pew Tactical, Snipercountry.com, and TTAG (The Truth About Guns), Mike is considered a firearms expert. His special area of expertise is handguns.
Mike is a long-time shooter. He has been punching paper targets, taking deer and other game and shooting at competitions since about 1975. Other related pursuits include reloading and bullet casting. He currently reloads for over 10 calibers, both handgun and rifle. His reloads, particularly for 9mm, were in great demand during the height of the ammo shortage among family and friends. He donated hundreds of rounds to informal shooting sessions. He was quoted as saying “I do not sell my reloads but I sure will help my guys shoot ’em for free!”. He has a few cherished firearms that he has inherited or otherwise procured — those are his favorites.
He earned B.S. and M.S. degrees from Indiana State University in 1974-1975.
He’s a firearm experts and is the founder of mhardesty.com.
